Lever 1
Planning and
Performance Management
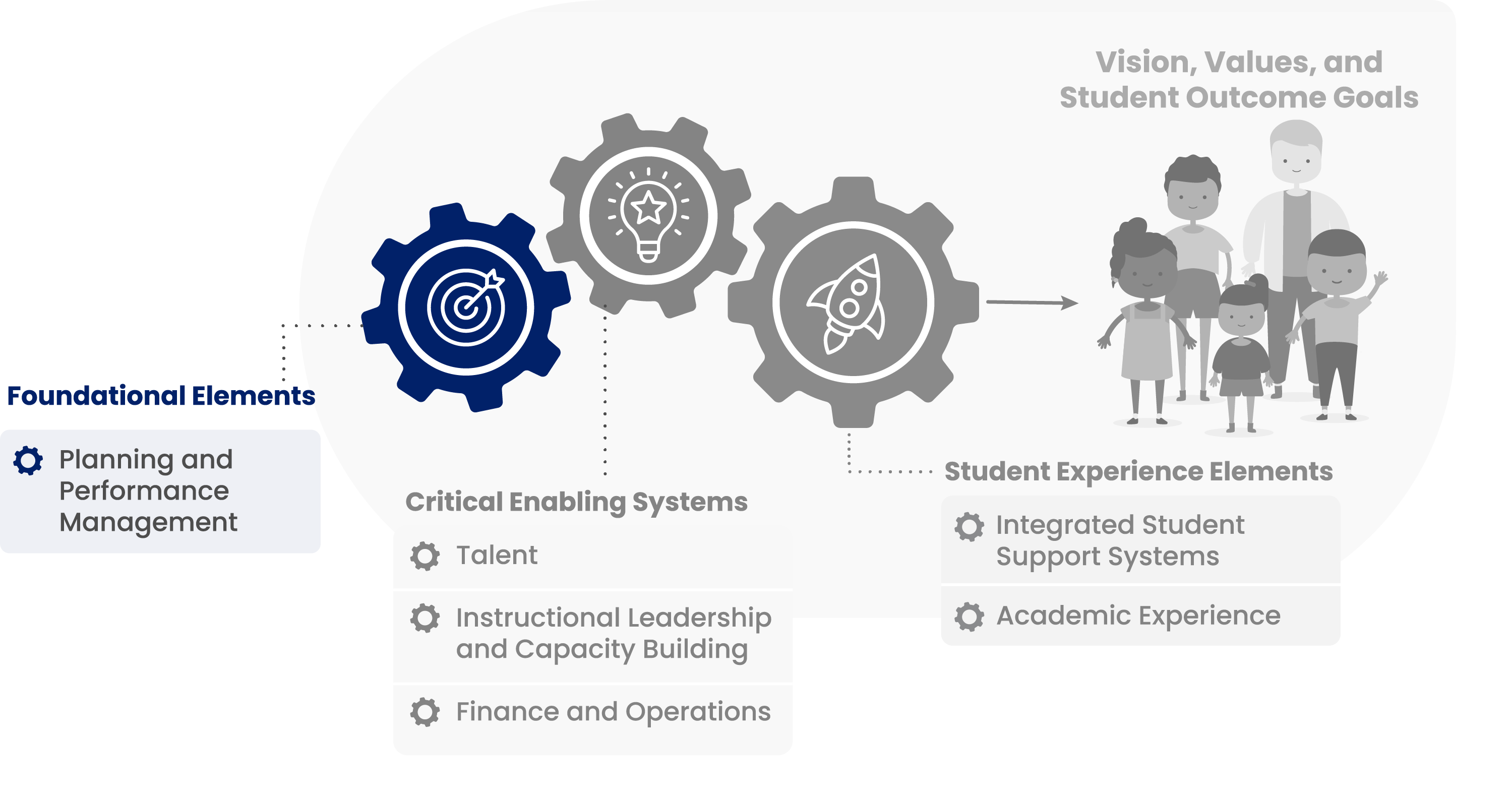
Lever 1: Planning and Performance Management
The district creates a clear and compelling vision for student success. It develops a strategic road map with key strategies and emphasizes the importance of implementation planning, project management, and continuous performance assessment. The district aims to instill a culture of ongoing improvement throughout the organization.
Board of Trustees Commitments:
Board commitments describe what the governance teams do to ensure that local education agency systems are set up for success. These commitments are under review and will be available soon.
1.1
1.1.1: Vision and Mission – District establishes and communicates a vision for student success and a mission informed by community needs and a valid, high-level understanding of what students need to succeed. +
Success Criteria
- Vision is anchored in student success, including ensuring students are college, career, and/or military ready and graduating prepared to be engaged, productive members of their communities.
- Vision is aligned on with district leadership team and board and includes stakeholder and community input.
- Mission is aligned on across district leadership team and board, clearly articulates the district’s role in delivering on the vision for all students and includes with stakeholder and community input.
1.1.2: Guiding Principles – District establishes and communicates guiding principles and commitments that will foster aligned continuous improvement mindsets and operating norms to achieve district’s vision. +
Success Criteria
- Guiding principles and commitments are written with stakeholder and community input collection as part of the process.
- Guiding principles and commitments at the district level demonstrate some alignment with student-facing guiding principles and commitments at campus levels.
- Guiding principles and commitments are communicated clearly and understandably, and they are easily accessible and visible to all stakeholders.
1.2
1.2.1: Central Performance Management Function – District establishes a Performance Management function with at least one central owner responsible for driving planning and performance management. +
Success Criteria
District designates a central owner whose role includes planning and performance management, including:
- Strategic planning: Laying out a process and plan for each step of Strategic Plan development (aligned to EA 2 steps and success criteria)
- Implementation planning and project management: Laying out a process and plan for each step of Implementation Planning & Project Management, as well as ensuring effective ongoing facilitation of project management (aligned to EA 3 steps and success criteria)
- Performance management: Centrally developing and managing a system for ongoing performance management routines (aligned to EA 4 steps and success criteria)
Central owner has dedicated time and resources to effectively execute planning and performance management central functions.
1.2.2: Goals – District Superintendent and Board of Trustees align on multi-year, student outcomes-focused top-line goals with the board of trustees and ensures awareness of goals with district and campus leaders and key internal and external stakeholders. +
Success Criteria
Top-line goals are specific, quantifiable, student outcome-focused goals that include:
-
- A population
- A five-year deadline (including a month and a year)
- Annual targets
- Annual student group targets
Top-line goals cover, at a minimum:
-
- Student academic performance in math
- Student academic performance in reading
- College, career, and military readiness outcomes
- Statutorily required goals
Goals are written such that they:
-
- Will challenge the organization
- Require adult behavior change
- Are influenceable by the superintendent
Superintendent and board collaboratively develop and align on goals.
Superintendent and board communicate goals with district and campus leaders and key internal and external stakeholders to build awareness.
1.2.3: Strategic Priorities – District articulates high-leverage strategic priorities in a coherent Theory of Action for accomplishing its vision for student success and goals. +
Success Criteria
District strategic plan includes 3-5 top priorities.
Strategic priorities encompass the highest leverage, research-based actions to improve the student experience.
Priorities are developed considering the student experience, the state of key district systems (e.g., talent, professional development, and capacity building), and stakeholder and community input.
1.2.4: Central Management and Systems Roadmap – District aligns central management philosophy and roadmap for key district systems (talent, academics, student support, etc.) to accomplish its strategic priorities and Theory of Action. +
Success Criteria
District leadership and board decide on the appropriate operating philosophy for district, including the degree of centralization of each key district system (talent, academics, student support, capacity building, and operations) between the central district and campus level, considering decision-making factors such as:
-
- Current performance of individual campuses (including academic performance and talent retention)
- Capacity of school leaders (particularly to execute any new or technically demanding strategic priorities independently)
- Capacity of teachers
- Capacity of central office
- Efficiency and scale benefits
- Unique community needs and demands (e.g., demands for unique school models that require autonomy in designing the student and staff experience)
1.2.5: Plan – District develops a coherent, multi-year strategic plan built on an analysis of the current state and aligned strategies. +
Success Criteria
Strategic plan effectively and compellingly articulates key components:
-
- Top-line goals
- Vision for the student experience
- High-level summary of the current state
- Strategic priorities driven by an understanding of the current state, research, and community needs
- Process includes community and stakeholder input, current state analysis, and research
- Plan includes a high-level timeline for accomplishing the goals
Strategic plan is used as a guiding document in district-level decision-making.
Strategic plan has been shared with the board, families, community members, and staff members in multiple channels (e.g., website, public presentations, town halls, etc.).
Board, community members, families, and staff members have had the opportunity to discuss the strategic plan with district leaders.
1.3
1.3.1: Implementation Planning – District develops clear implementation plans with roles, responsibilities, timelines, and project management structures. +
Success Criteria
Implementation plans are developed for each strategic priority that articulate:
-
- Key milestones and deliverables on a timeline
- Activities leading to key milestones, anchored in timelines
- Roles and responsibilities, including clarity on owners, other key contributors, and decision-making rights
- Routine project management meeting structures appropriately spaced across the timeline (minimum biweekly cadence recommended for high-priority initiatives) to ensure effective progress tracking, troubleshooting, and escalation of issues
Implementation plans are developed and stored such that they are dynamic, accessible for staff, and easy for teams to update.
Each strategic priority includes an identified implementation team with an owner and representatives at the district, campus, and classroom level.
1.3.2: Project Management – District ensures project management meeting structures and tools are developed and used to ensure on-time, high-quality completion of milestones and deliverables, as well as accountability for project progress. +
Success Criteria
Routine project management meetings with key staff are scheduled at least biweekly (for high-priority initiatives) to ensure effective progress tracking and issue resolution.
Project management meeting structures include:
-
- Overall implementation plan and its alignment to the broader strategic plan, vision, and goals
Review of updated status of progress toward milestones and deliverables - Escalation of issues and barriers
- Collective troubleshooting of issues and naming of next steps
- Naming when project plans, or approaches need to be changed given evolving circumstances or status
- Overall implementation plan and its alignment to the broader strategic plan, vision, and goals
Project management tools are user-friendly, accessible, and provide essential features for tracking and updating activity status and roles.
1.4
1.4.1: Initiative Goals and Measurement Plan – District continuously improves implementation by reflecting on progress against goals and plan. +
Success Criteria
Metrics (qualitative and quantitative) selected for implementing performance management are well-aligned to and effectively encompass the initiative’s key drivers of success.
District has a measurement plan that:
-
- Was developed to encompass high-priority strategies
- Includes metrics for key inputs, outputs, and outcomes
- Has aligned goals, collection timing, and defined roles
- Tracks progress throughout the initiative
Implementation goals align with Goal Progress Measures (GPMs) developed for board and superintendent alignment and reporting.
The measurement plan’s cadence of collection aligns with key annual events (e.g., teacher coaching, PD timelines, and budget decisions) to drive management actions.
Leadership communicates implementation goals and messages their importance for driving management action, with a particular emphasis on the key inputs and outputs necessary for successful implementation.
1.4.2: Data Setup – District assesses current data systems and bolsters capacity, and systems as needed to meet measurement and monitoring needs. +
Success Criteria
District clearly outlines how current data systems (both qualitative and quantitative), and collection practices meet the needs of the highest-priority strategies in the measurement plans.
District implements solutions to fill gaps in data systems to deliver on measurement plans, including:
-
- Developing new/additional data collection tools or adding data items to existing tools
- Adjusting the cadence of the collection
- Updating and/or revising current data systems and infrastructure
- Setting clear roles, responsibilities, and expectations for accurate collection of new or revised data items
1.4.3: Data Collection – District collects and synthesizes data and information related to progress in executing implementation plan and achieving the district’s vision and goals. +
Success Criteria
All key input, output, and outcome measures are collected and synthesized on a cadence aligned with the measurement plan and timeline for driving management action/iteration on implementation (e.g., informing next teacher professional development).
Data is reported clearly and at a level of breakdown (e.g. by campus, grade level, student subgroup, etc.) that is appropriate to effectively support management in assessing implementation quality and identifying steps for improvement.
Data includes any critical qualitative context that would support understanding of data/status and drive action (e.g., low number of students in a given sample).
District shares data in a format aligned to the district performance management routine structures.
1.4.4: Performance Management Routines – District establishes systems that routinize initiative progress reflection and iteration on implementation tactics, as needed. +
Success Criteria
District sets cadence for regular performance management reflection for each strategic priority area, recommended at least three times per year and are timed to align with key management actions (e.g. teacher coaching, professional development, and budget decisions).
District performance management routines:
-
- Include relevant data, key insights, and questions for reflection
- Focus on analyzing input and output measures to drive management action to improve implementation
- Include district leadership and staff leading implementation
District reflects on implications of performance management routine insights for longer-term strategic plan and theory of action and (sparingly) adjusts the long-term plan as needed to better meet student outcome goals.
1.5
1.5.1: Roles – District creates clear roles, responsibilities, and expectations for performance management routines. +
Success Criteria
District clearly sets and communicates roles for each key facet of effectively executing performance management routines for each top district priority and aligned initiative, including:
-
- Who develops plans
- Who regularly maintains and project manages against plans
- Who collects and synthesizes data for performance management routines
- Who prepares agenda/materials for performance management routines
- Who facilitates performance management routines
Who attends and contributes to performance management routines - Who has approval and/or veto power on any implementation plans and measurement plans (inclusive of goals)
District communicates with campus leadership or other initiative owners to ensure an aligned approach across performance management routines.
1.5.2: Capacity Building – District provides leadership training and ongoing support to execute performance management actions. +
Success Criteria
District clearly outlines the overall rationale for why performance management is critical to the district’s approach and meeting strategic plan objectives.
District provides onboarding onto performance management roles, expectations, best practices, and processes to all district staff members expected to participate in/contribute to performance management.
District leaders are trained in their roles and key actions within performance management structures, particularly using a systems lens to performance manage and understanding the interconnected actions needed across district systems to drive impact.
1.5.3: Mindset and Culture – District cultivates continuous improvement mindsets and culture supportive of effective performance management and strategic plan execution via communications, training, and key district structures. +
Success Criteria
District establishes a performance management model focused on systems thinking, including an understanding root causes, data points, and current status of initiatives.
District routines include change management best practices and a continuous improvement orientation which requires growth mindset and ownership.
District has performance management routines that consistently include opportunities for authentic engagement of teammates in decision-making.
1.5.4: Continuously Improving the Performance Management System – District continually assesses and addresses performance management practices to identify challenges, needs, and opportunities for improvement. +
Success Criteria
District leadership and central owner driving performance management assess the degree to which performance management structures are effective, identify areas for improvement, and execute improvements as needed.
District establishes opportunities to gather feedback from relevant stakeholders regarding the effectiveness of performance management routine structures.

